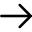
| Indian Constitution | Main sources of the indian Constitution |
| Australian Constitution | Concurrent List, Freedom of trade, commerce and intercourse joint sitting of the two Houses of Parliament |
| British Constitution | Parliamentary government, Rule of Law, Legislative procedure, Single citizenship, Cabinet System, Prerogative Writs. |
| Canadian Constitution | Federation with a strong center, residuary powers with the center, appointment of state governors by the center and advisory jurisdiction of the Supreme Court. |
| French Constitution | Republic and the ideals of liberty equality and fraternity in the Preamble. |
| Government of India Act, 1935 | Federal Scheme, Office of Governor, Judiciary, Public Service Commissions, Emergency provisions, Administrative details. |
| Irish Constitution | Directive Principles of State Policy, nomination of members to Rajya Sabha and method of election of President, Federation with a strong center, Vesting of residuary powers in the Center, appointment of State Governors by the Centre and advisory jurisdiction of the Supreme Court. |
| Japanese Constitution | Procedure established by law. The drafted Constitution was finally adopted on November 26, 1949. |
| South African Constitution | Procedure for amendment, the Constitution and election of the members of Rajya Sabha. |
| Soviet Constitution | Fundamental duties, the ideal of justice (social, economic and political) in the Preamble |
| US Constitution | Fundamental Rights, Independence of Judiciary, Judicial Review, Impeachment of the President, Removal of Supreme Court and High Court judges and post of Vice-President. |
| Weimar Constitution | Suspension of Fundamental Rights during Emergency. |
The main sources of the Indian constitution (GK in English)
Posted on: 11/06/2017 07:53:00 AM
By: Team RIJADEJA.com